Beautiful Info About How To Check File Descriptors

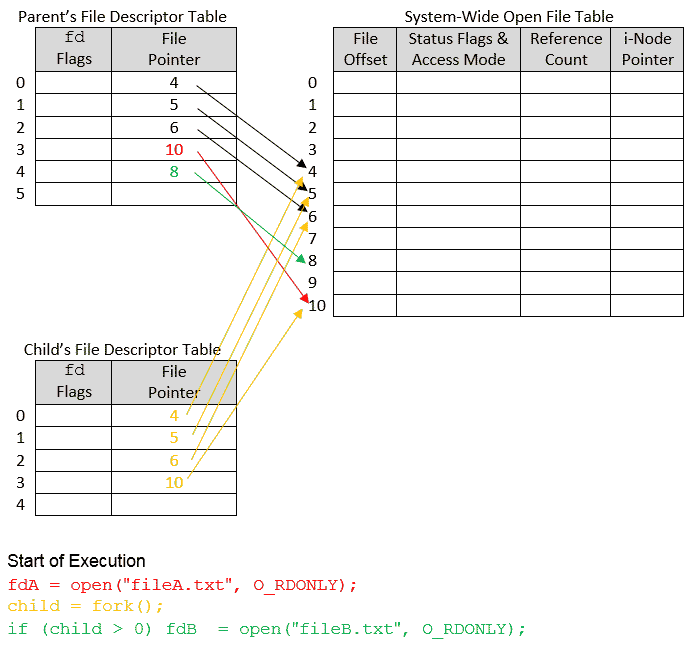
Now i want to check whether var1 (which still holds the opened descriptor) is still valid.
How to check file descriptors. Each open call will get a file descriptor as a return value (there are also other apis that can return file descriptors. Step # 1 find out pid. Thus, we have to determine.
Exec 3> file 4>&3 5> file 6>>. $ ps aux | grep gedit. Step # 2 list file opened by a pid # 28290.
The basic steps would be: Or you can use one of the other functions that take a file descriptor as an argument, looking for ebadf (bad file. # ps aux | grep mysqld.
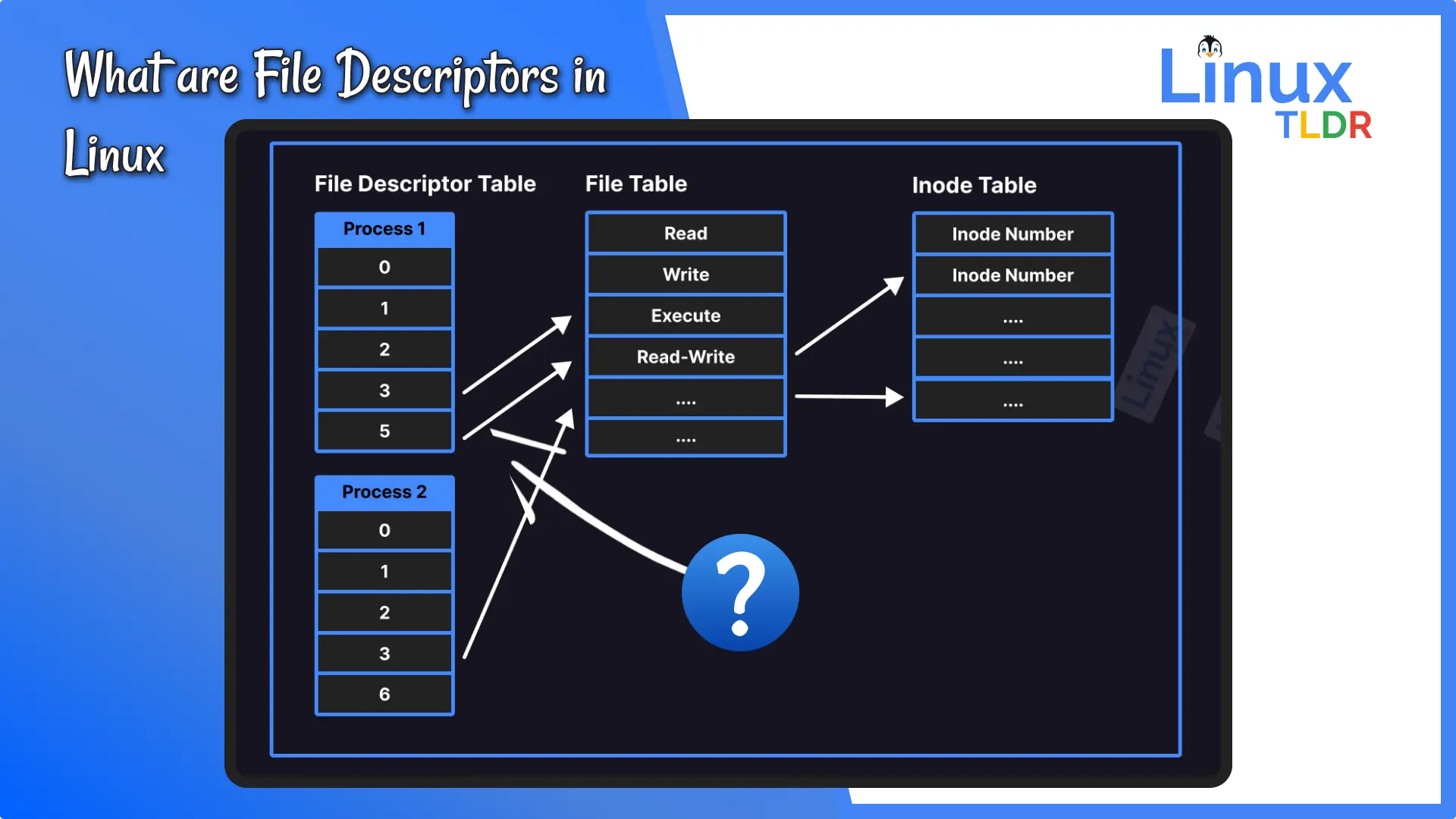
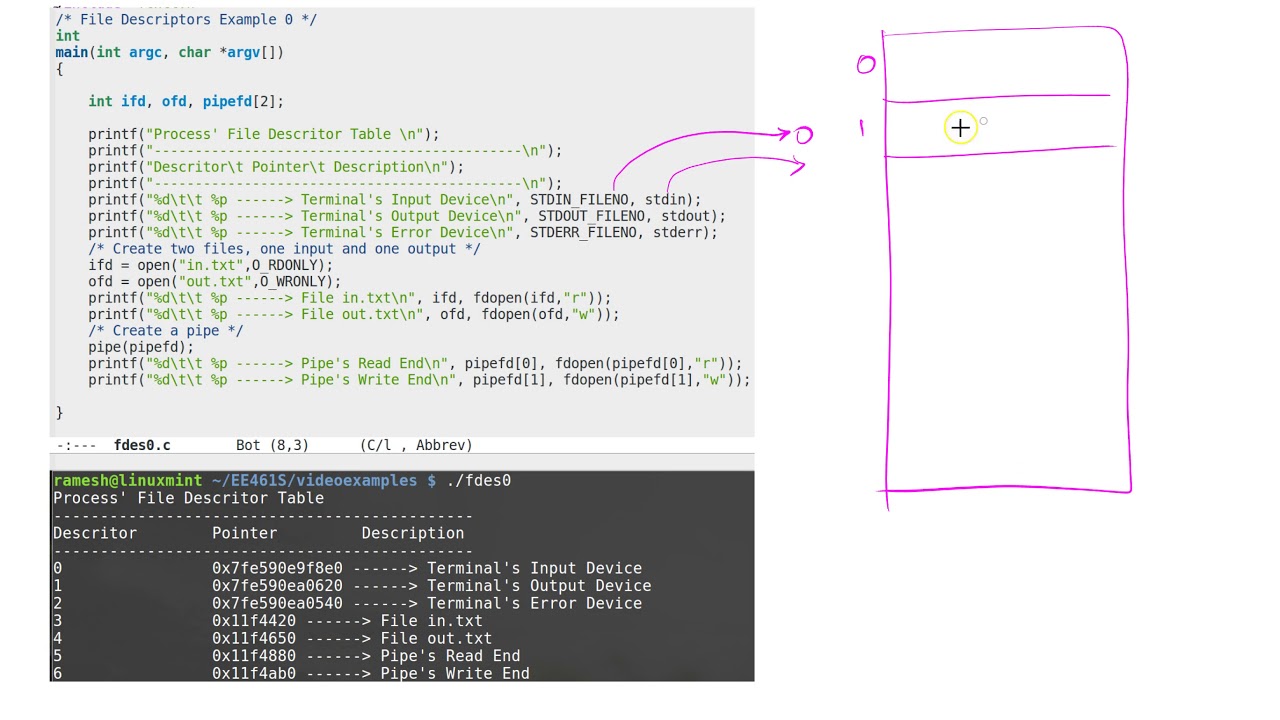
Fprintf(stderr, i'm writing to stderr\n); There is no such thing as the file descriptor for a file. You get a file descriptor (let’s say fd = 3 ).
Modified 3 years, 4 months ago. The z option tells docker that two containers share the volume content. Replace “ gedit ” with your.
We can use the ulimit command to set or get the resource limits of the current user: In a posix environment when using system calls to manipulate text files ( open (), close (), read (), write () ), is there a way to to check to see if i actually closed a. You can use fstat () to check if a file descriptor is open.
In the /proc pseudo filesystem, we can find the open file descriptors under /proc/<<strong>pid</strong>>/fd/ where is the pid of a given process. Use the lsof command or /proc/$pid/ file system to display open fds (file descriptors), run: Finally, close the file using fd.
Use fd to read/write data. To find out pid for mysqld process, enter: We see unlimited in the output when we run ulimit.
Asked jul 24, 2013 at 8:52. The above number shows that user. First, find out your process identifier (or pid) using the ps command before viewing the file descriptors under it.
These suffixes tell docker to relabel file objects on the shared volumes. Take a look at the following c program: $ ps aux | grep i3.